Search Results for: intensity
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
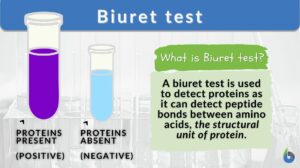
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Abiotic and Biotic Factors
Abiotic factors are essentially non-living components that affect the living organisms of the freshwater community. When... Read More
Running Water Freshwater Community Factors
This tutorial continues from the previous one, which introduced lotic (running water) communities. Here, some of the... Read More
Chemokinesis
Definition noun A behavioral response of a cell or an organism to a soluble chemical that leads to random or directionally... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
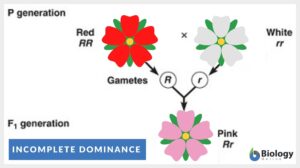
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete Dominance Definition After Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance laws, the term ''incomplete dominance'' was... Read More
Graded potential
Definition noun, plural: graded potentials A change in the electrical potential on the membrane of an excitable cell (e.g. a... Read More
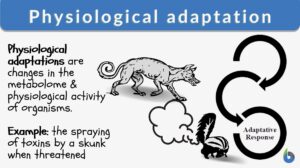
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
Subliminal stimulus
Definition noun, plural: subliminal stimuli (physiology) A stimulus inadequate to generate an action potential and thereby... Read More
Density dependence
Definition noun (population ecology) An effect in which the intensity changes with the increasing population density, e.g.... Read More
Isodynamic
Isodynamic Of, pertaining to, having, or denoting, equality of force. (Science: physiology) isodynamic foods, those foods... Read More
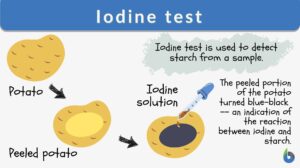
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Supraliminal stimulus
Definition noun, plural: supraliminal stimuli A stimulus above the threshold of sensation or of awareness Supplement In... Read More
Primer extension
Definition noun A method that uses the enzyme Reverse Transcriptase (RNA-dependent DNA polymerase) to determine the... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Androsterone
Definition noun, plural: androsterones A steroid hormone, with a chemical formula of C19H30O2, has masculinizing effects,... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Freshwater Communities & Plankton
Plankton are microscopic organisms that live suspended in the water environment and form a very important part of the... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the means that primary producers (mostly plants) can obtain energy via light energy. The energy gained... Read More
Staircase phenomenon
staircase phenomenon --> treppe A phenomenon in cardiac muscle first observed by H.P. Bowditch; if a number of stimuli of... Read More
Unconditioned stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus inherently triggers an automatic response, not reliant on deliberate prior learning. In contrast... Read More
Susceptibility
susceptibility Origin: Cf. F. Susceptibilite. 1. The state or quality of being susceptible; the capability of receiving... Read More
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More