Search Results for: output
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Negative feedback
Definition noun (1) A feedback in which the system responds to the perturbation in the opposite direction as the... Read More
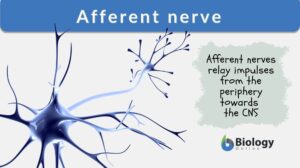
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
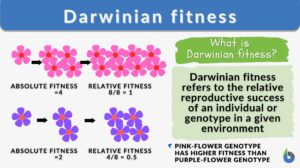
Darwinian fitness
Darwinian Fitness Definition Darwinian fitness refers to the measure of an individual organism's or genotype's reproductive... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Online systems
online systems systems where the input data enter the computer directly from the point of origin (usually a terminal or... Read More
Adrenaline
A catecholamine secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress (trade name Adrenalin); stimulates autonomic nerve... Read More
Dependent variable
Definition noun, plural: dependent variables (mathematical modeling) The variable in a functional relation whose value is... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
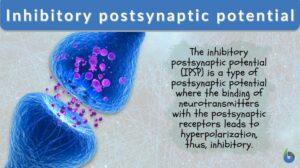
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
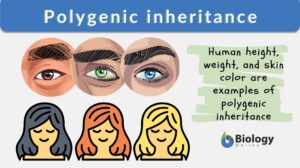
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Somatic nervous system
Definition noun The part of the peripheral nervous system that consists of afferent nerves responsible in relaying motor... Read More
Oligohydramnios
Definition noun A condition characterized by a deficiency of amniotic fluid Supplement The amniotic fluid is the fluid that... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Imprinting
What does imprinting mean? Have you watched the TV cartoon show “Tom and Jerry” with an episode of a duck and its... Read More
Milk yields affected by music tempo
Dairy cows produce more milk when listening to REM's 'Everybody Hurts' or Beethoven's 'Pastoral Symphony' than when... Read More
Bondok’s Classification of the Thalamic Nuclei
Anatomists usually classify the thalamic nuclei according to their relation to the internal medullary lamina into 5 groups:... Read More
Accumulation
Accumulation The action or process of accumulating, state of being or having accumulated, a collecting together. (Science:... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Elution profile
Definition noun A time-based graphic output of the chromatograph which shows how much material is being carried out of the... Read More
Degenerate
Degenerate means to become worse or less of its kind or former state. In biology, it means an entity performs the same... Read More
Photorespiration
Definition noun (1) The process by which in the presence of light plant consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide (in... Read More
Wood units
Wood units A simplified measurement of pulmonary vascular resistance that uses pressures instead of more complicated units... Read More