Search Results for: passage
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
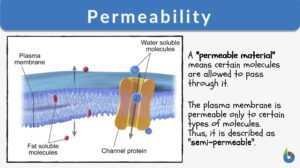
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
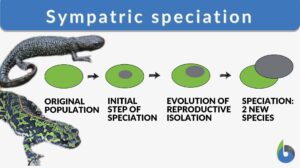
Sympatric speciation
Speciation is a process of evolution through which two different existing populations evolve and a distinct species form. It... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Dead Man Walking
Dead Man Walking: Wade Davis and the Secret of the Zombie Poison By Patrick D. Hahn Accepted on September 4, 2007 Twenty... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Nuclear pore
Definition noun plural: nuclear pores ˈnu kli ər, pɔː Any of the many perforations on the nucleus as a result of the... Read More
Electrical synapse
Definition noun A form of synapse between two apposed neurons in which nerve impulse transmission is rapid and occurs by... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
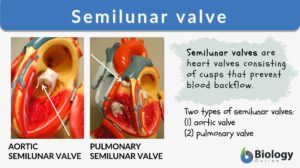
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Blood-brain barrier
Definition noun A semipermeable membrane that serves as a selective barrier separating the circulating blood and the... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
How High Sugar Level in Blood Damages the Blood Vessels
By Vicki Mozo Damage in the vasculature is common in individuals who have high sugar level in blood. It seems that an... Read More
Determination
Determination (Science: cell biology) The committment of a cell to a particular path of differentiation, even though there... Read More
Transmission
transmission 1. (Science: microbiology, physiology) A passage or transfer, as of a disease from one individual to another or... Read More