Search Results for: pores
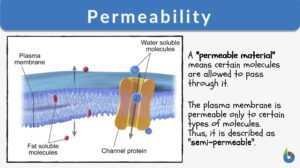
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Nuclear pore
Definition noun plural: nuclear pores ˈnu kli ər, pɔː Any of the many perforations on the nucleus as a result of the... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Millepora alcicornis
Millepora alcicornis is a species of the family Milleporidae, class Hydrozoa, phylum Cnidaria. It is a colonial fire coral... Read More
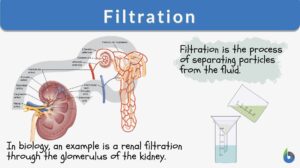
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
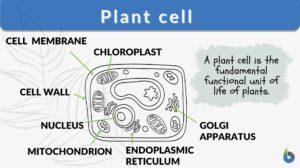
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Electroporation
Definition noun, plural: electroporations A non-chemical method that transfers the genetic material into the recipient cell... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Nucleoporin
Definition noun plural: nucleoporins Any of the family of porins that make up the nuclear pore complex Details Overview... Read More
Sonoporation
Definition noun A mechanical method of delivering molecules into the cell using sound, e.g. ultrasonic... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Pneumatophore
Definition noun, plural: pneumatophores (botany) A specialized aerial root, such as in certain mangrove species, that stick... Read More
Liliopsida
Definition noun (plant taxonomy) A taxonomic class of the division Magnoliophyta comprised of lilies, grasses, palms,... Read More
Sieve element
Definition noun (botany) A food-conducting cell in the phloem of vascular plants Supplement The phloem is the vascular... Read More
Sieve tube
Definition noun, plural: sieve tubes (botany) Any of the tubes in the phloem comprised of cells joined end-to-end through... Read More
Sieve-tube element
Definition noun, plural: sieve tube elements A specialized type of sclerenchyma cell that forms a sieve tube of... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
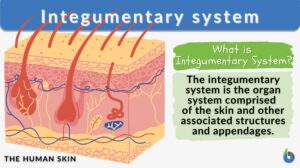
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Perspiration
Definition noun (1) The act or the process of producing and excreting a watery, saline fluid that evaporates from the... Read More