Search Results for: rigidity
Lead-pipe rigidity
Definition noun A hypokinetic disorder characterized by the inflexibility or stiffness of the limb that is maintained... Read More
Clasp-knife rigidity
Clasp-knife rigidity --> clasp-knife spasticity initial increased resistance to stretch of the extensor muscles of a joint... Read More
Decerebrate rigidity
Definition noun An involuntary posturing whereby the arms are extended on the sides while the head is arched back, as... Read More
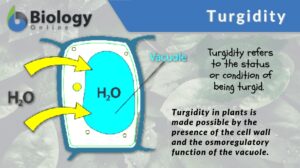
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
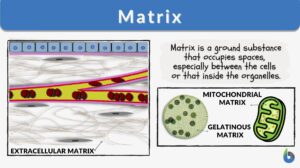
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Glycosidase
Definition noun, plural: glycosidases (biochemistry) An enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of a... Read More
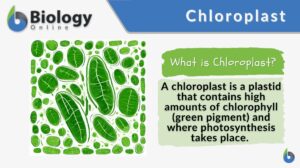
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Secondary cell wall
Definition noun plural: secondary cell walls ˈsɛkənˌdɛɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms... Read More
Middle lamella
Definition noun plural: middle lamellae ˈmɪdəl ləˈmɛl.ə A pectin-rich intercellular material that glues the... Read More
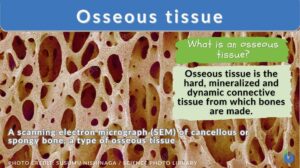
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Spongy bone
Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is a type of bone tissue found at the ends of long bones and... Read More
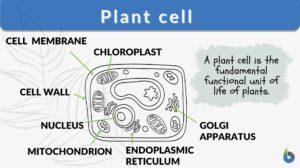
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives
These plants are seedless plants, but unlike the bryophytes, they do have vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Because of the... Read More
Control of Body Movement
Motor Control Hierarchy A motor program is the pattern of neural activities required to perform a movement is created and... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
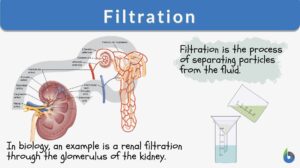
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Primary cell wall
Definition noun plural: primary cell walls ˈpɹaɪməɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms prior to... Read More
Postmortem
postmortem 1. After death; as, postmortem rigidity. Pertaining to or occurring during the period after death. 2.... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More