Search Results for: sides
Bilateral symmetry
Definition noun, plural: bilateral symmetries A form of symmetry in which the opposite sides along a midline is a duplicate... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
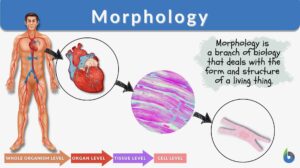
Morphology
Morphology Definition Morphology means the study of the shape and structure of living things from a biological perspective.... Read More
Decerebrate rigidity
Definition noun An involuntary posturing whereby the arms are extended on the sides while the head is arched back, as... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
Radial symmetry
Definition noun A form of symmetry in which the body plan is divisible into identical parts around a central... Read More
Lateralization
Definition noun Localization of a function or activity on one side of the body in consistent preference to the... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
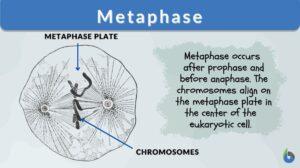
Meiosis II
Definition The second of the two consecutive divisions of the nucleus of eukaryotic cell during meiosis, and composed of the... Read More
Bronchopulmonary lymph node
Definition noun, plural: bronchopulmonary lymph nodes Any of the many lymph nodes located in the hilum of each lung, and... Read More
Monocular vision
Definition noun (1) (zoology) A type of vision in which one eye of the animal moves and sees objects independently of the... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Microtubule organizing center
Definition noun A structure inside the cell from where microtubules organize following depolymerization to turn into tubular... Read More
Bipennate muscle
Definition noun A type of pennate muscle wherein the muscle fibers or fascicles are in opposite sides of the central... Read More
Lateral meristem
Definition noun, plural: lateral meristems (botany) A type of meristematic tissue comprised of meristematic cells in the... Read More
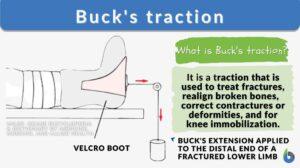
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Book lungs
Book Lungs Definition Lungs are known as the organs that help organisms breathe. When we think of lungs, we think of the... Read More
Transmembrane proteins
transmembrane protein (Science: cell biology) A protein subunit in which the polypeptide chain is exposed on both sides of... Read More
Diatomaceous earth
Definition noun A type of silica-rich dirt which is soft, fine-grained, porous, light-coloured, and composed of the... Read More
Anatomical plane
An anatomical plane refers to a hypothetical plane used in describing the location of bodily structures or movement... Read More
Men could go extinct? Y chromosome disappearing slowly
Hold on to your seats, gentlemen -- the male chromosome (Y chromosome) disappearing at a certain rate could absolutely be... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
Examples of Natural Selection
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Darwin's Finches Darwin's finches are an excellent example of the way in... Read More