Search Results for: susceptibility
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Susceptibility
susceptibility Origin: Cf. F. Susceptibilite. 1. The state or quality of being susceptible; the capability of receiving... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Sensibility
sensibility Origin: Cf. F. Sensibilite, LL. Sensibilitas. 1. (Science: physiology) The quality or state of being sensible,... Read More
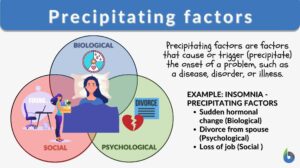
Precipitating factors
Precipitating Factor Definition Precipitating factors are factors that initiate or promote the onset of any illness,... Read More
Genetic diversity
Genetic Diversity Definition Each species is composed of individuals with their own set of genes. A gene is the inheritance... Read More
Redundancy Hypothesis
Definition noun A theory that assumes one or more species impart a role within an ecological unit to maintain dynamic... Read More
Opsonization
Definition noun, plural: opsonizations The process at which opsonins bind to the surface of the antigen so that the... Read More
Polygenic trait
Polygenic Trait Definition Polygenic trait refers to a trait that is controlled by multiple non-allelic genes. These genes... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
Physical Development in Humans
The Newly Born Child Depending on the nutrients available to the child within pregnancy and the genetic makeup of the... Read More
Neisseria mucosa
Definition Noun A gram-negative mucoid cocci bacterium involved in several human infections including cerebrospinal fluid... Read More
Haemophilus parahaemolyticus
Definition Noun A gram-negative commensal bacterium involved as a causative agent in some human diseases including... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
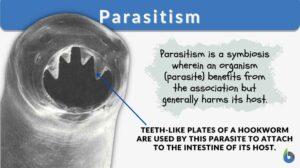
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
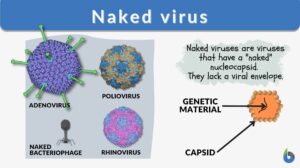
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Colony-forming unit
Colony Forming Unit Definition A Colony Forming Unit (CFU) in microbiology and cellular biology refers to a measure of... Read More
Adverse effects
Adverse effect this is an abnormal or harmful effect to an organism caused by exposure to a chemical. It is indicated by... Read More
Desiccation
Desiccation definition Desiccation refers to the state, the act, or the process of removing or extracting water content... Read More
Irritability
Definition noun (physiology) The ability of the cell to receive and respond to a stimulus. (pathology) The excessive... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
The Psychobiology of Hysteria
Editorial Hysteria is often regarded as the archetypal psychodynamic illness. Freud carried out much of his early work on... Read More
Fragmentation
Fragmentation Definition What is fragmentation? In general, fragmentation refers to the state or the process of breaking... Read More