Search Results for: air
Air pressure
Definition noun (1) The pressure caused by the weight of air. (2) The force exerted by air per unit area. Supplement Air... Read More
Ethmoid air cells
Definition noun The numerous tiny-walled, fluid-filled cells that lie in the ethmoid bone of the skull (i.e. specifically... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Air bladder
Air bladder 1. (Science: anatomy) An air sac, sometimes double or variously lobed, in the visceral cavity of many fishes. It... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
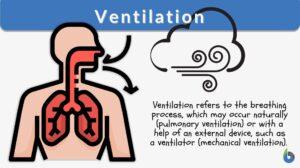
Ventilation
Ventilation Definition Often when persons think of ventilation, they think of getting clean or enough air into a room. This... Read More
Blood-air barrier
Blood-air barrier The barrier between capillary blood and alveolar air comprising the alveolar epithelium and capillary... Read More
Supplemental air
Definition noun The additional volume of air exhaled with maximum effort at the end of a normal, quiet... Read More
Air Pollution
Pollution of the atmosphere; air pollution reduced the visibility.An abiotic Factor, air Pollution is any substance that has... Read More
Residual air
Definition noun The amount of air that remains in the lungs following a maximal expiration. Supplement The residual air that... Read More
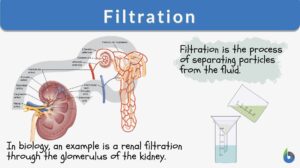
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Air conduction
Air conduction in relation to hearing, the transmission of sound to the inner ear through the external Auditory Canal and... Read More
Complementary air
Definition noun The amount of air that can be drawn maximally into the lungs after a normal, quiet... Read More
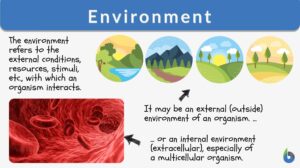
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More
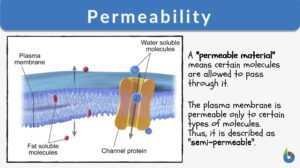
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Ethmoidal labyrinth
Definition noun, plural: ethmoidal labyrinths Either of the paired lateral masses of the ethmoid bone, consisting of the... Read More
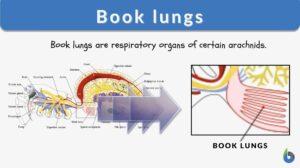
Book lungs
Book Lungs Definition Lungs are known as the organs that help organisms breathe. When we think of lungs, we think of the... Read More
Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in the freshwater community provide a means of food for herbivores and harness new energy into the community as a... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Contamination
Contamination Definition Contamination, sometimes interchanged with pollution, is the existence of live things or... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Pneumatophore
Definition noun, plural: pneumatophores (botany) A specialized aerial root, such as in certain mangrove species, that stick... Read More
The Water Cycle
The water cycle (sometimes referred to as the hydrological cycle) is the continuous transfer of water from air, sea land and... Read More