Search Results for: elements
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Tracheary elements
Definition noun (botany) The principal conductive cells of the xylem associated with the conduction of water and minerals... Read More
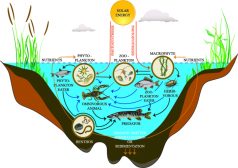
Freshwater Producers and Consumers
There are four main constituents of the living environment that form the freshwater ecosystem, they are as follows. ... Read More
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Sieve-tube element
Definition noun, plural: sieve tube elements A specialized type of sclerenchyma cell that forms a sieve tube of... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Origins of Life on Earth
Although Earth was created around 4.5 billion years ago, life began to exist not long after. Due to the huge timescales... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
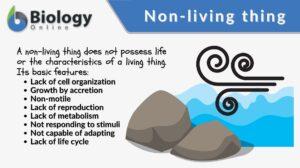
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Xylem vessel
Definition noun, plural: xylem vessels (botany) One of the tracheary elements of xylem that is characterized by being made... Read More
Still Water Community Plants
Freshwater Plants & Water As mentioned in the previous tutorial about still water plants, the method of transpiration... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
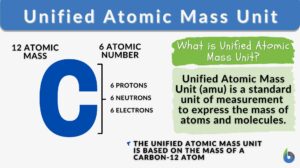
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
SELFISH GENE – selfish to persist
What is a selfish gene? A selfish gene is not a gene that makes an individual selfish. In fact, it may even be involved in... Read More
Retrotransposon
Definition noun, plural: retrotransposons A transposon that is amplified via reverse transcription, i.e. the DNA element is... Read More
Interspersed repeat
Definition noun, plural: interspersed repeats A type of repeated sequence in which the copies are dispersed throughout the... Read More
Sieve tube
Definition noun, plural: sieve tubes (botany) Any of the tubes in the phloem comprised of cells joined end-to-end through... Read More
Young-helmholtz theory of colour vision
'''Young-helmholtz theory of color vision A theory that there are three perceiving elements in the retina: red, green, and... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More