Search Results for: gap
Gap 2-M DNA damage checkpoint
Definition noun (cell biology) A control mechanism in G2 phase of the cell cycle that ensures the cell is ready for cell... Read More
Gap junction
Definition noun, plural: gap junctions A type of cell junction characterized by the intercellular channel that is formed in... Read More
Gap 0 phase
Definition noun The phase in the cell cycle wherein the cell is in inactive or non-cycling state following cell... Read More
Gap 2 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase of the cell cycle wherein the cell continues to grow and then... Read More
Gap 1 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) The first period in the interphase wherein the cell primarily grows in cell... Read More
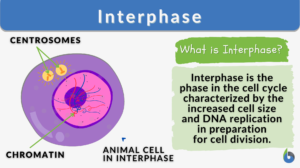
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
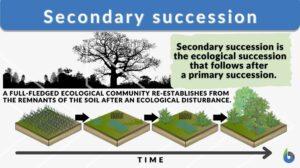
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Synthesis phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase wherein the cell primarily duplicates its DNA via... Read More
Mitotic phase
Definition noun The phase in the life cycle of a cell highlighted by chromosomal separation resulting into two identical... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Cell junction
Definition noun, plural: cell junctions Intercellular connections between adjacent cells, resulting in varying degrees of... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Pair-rule gene
Definition noun A segmentation gene whose expression subdivides the embryo into a series of stripes, and sets the boundaries... Read More
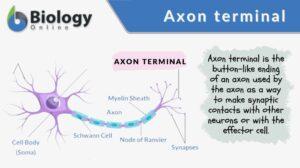
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Electrical synapse
Definition noun A form of synapse between two apposed neurons in which nerve impulse transmission is rapid and occurs by... Read More
Anchoring junction
Definition noun, plural: tight junctions A type of cell junction that is attached to components of the extracellular... Read More
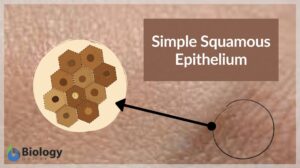
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives
These plants are seedless plants, but unlike the bryophytes, they do have vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Because of the... Read More
Perinuclear space
Definition noun plural: perinuclear spaces per·i·nu·cle·ar space The space or gap between the inner and outer... Read More
The Water Cycle
The water cycle (sometimes referred to as the hydrological cycle) is the continuous transfer of water from air, sea land and... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
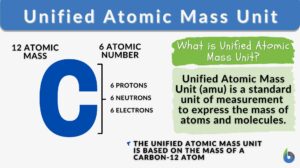
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Atrial syncytium
Definition noun A network of cardiac muscle cells connected by gap junctions that allows coordinate contraction of the... Read More