Search Results for: impulses
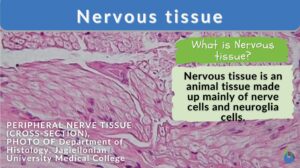
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
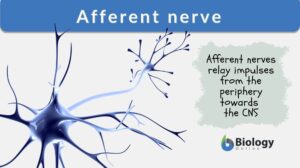
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
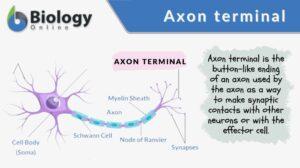
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Afferent neuron
Definition noun, plural: afferent neurons A type of neuron that detects stimulus from the periphery and relays nerve... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Interneuron
Definition noun, plural: interneurons (1) Any local circuit neuron of the central nervous system that relays impulses... Read More
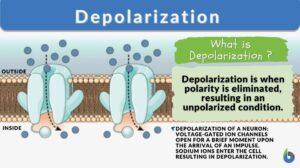
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Efferent nerve
Definition noun, plural: efferent nerves The type of nerve that carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system... Read More
Efferent neuron
Definition noun, plural: efferent neurons A neuron with an axon that carries nerve impulses peripherally, and innervates... Read More
Sense organ
Definition noun, plural: sense organs An organ or structure that has nerve endings capable of detecting and reacting to a... Read More
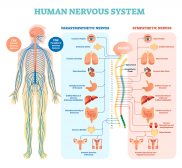
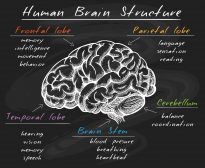
The Human Nervous System
The nervous system is essentially a biological information highway, and is responsible for controlling all the biological... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Bell-Magendie law
Definition noun The principle referring to the separation of sensory and motor neurons of the spinal cord, where the... Read More
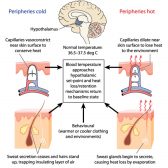
Temperature Regulation in Animals
Control of Temperature in Homeotherms Animals capable of temperature regulation within a given range are deemed homeotherms... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
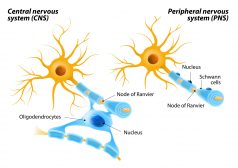
The Central Nervous System
Myelin Sheath Myelin is a substance that forms the myelin sheath associated with nerve cells. This sheath is a layer of... Read More
The Conscious & Unconscious Nervous System
The Central Nervous System is arguably the most important part of the body because of the way it controls the biological... Read More
Transmission
transmission 1. (Science: microbiology, physiology) A passage or transfer, as of a disease from one individual to another or... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Gap junction
Definition noun, plural: gap junctions A type of cell junction characterized by the intercellular channel that is formed in... Read More
Sensory neuron
Definition noun, plural: sensory neurons A type of neuron that transmits sensory nerve impulses Supplement The neurons are... Read More
Somatic nervous system
Definition noun The part of the peripheral nervous system that consists of afferent nerves responsible in relaying motor... Read More
Phenylalanine
phenylalanine (Science: amino acid) One of the amino acids which the body cannot manufacture itself, but must acquire from... Read More
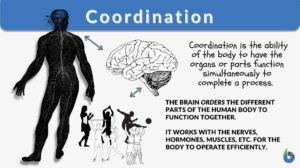
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Reverberating circuit
reverberating circuit A theory of periodic conduction through the cerebral cortex of trains of impulses traveling in... Read More