Search Results for: mineral
A Balanced Diet – Minerals and Proteins
Minerals Various minerals in the Earth's crust are required for a healthy balanced diet. These inorganic compounds have... Read More
Mineral soil
mineral soil (Science: ecology) Any soil consisting primarily of mineral (sand, silt and clay) material, rather than organic... Read More
Mineralization
mineralization 1. The process of mineralizing, or forming a mineral by combination of a metal with another element; also,... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
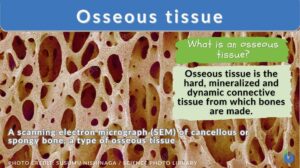
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Magnetosome
Definition noun, plural: magnetosomes A membranous cytoplasmic structure containing mineral crystals that enable certain... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Spongy bone
Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is a type of bone tissue found at the ends of long bones and... Read More
Petrified Wood : The World of Fossilized Wood, Cones, Ferns, and Cycads
Petrified Wood : The World of Fossilized Wood, Cones, Ferns, and Cycads ... Read More
Bone tissue
Definition noun, plural: bone tissues A mineralized connective tissue from which bones are made. Supplement The bone tissue... Read More
Tracheary elements
Definition noun (botany) The principal conductive cells of the xylem associated with the conduction of water and minerals... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Osteoporosis
Definition noun, plural: osteoporoses A disease of bone in which the bones become extremely porous and are subject to... Read More
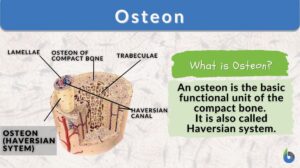
Compact substance
Definition noun A type of osseous tissue consisting of closely packed osteons or haversian systems, and forms the extremely... Read More
Compact bone
Definition noun, plural: compact bones A type of osseous tissue consisting of closely packed osteons or haversian systems,... Read More
Still Water Animals
Through millions of years of evolution, animals living in an aquatic environment have diversified to occupy the ecological... Read More
Inorganic molecule
Definition noun, plural: inorganic molecules (1) A molecule not consisting of carbon atoms. (2) Any molecule that is not... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Carrying capacity
Carrying Capacity Definition What is carrying capacity? In biology and environmental science, the carrying capacity of a... Read More
Plant Meristems and Growth
A common mistake that many people assume is that an increase in size means an increase in growth. This is not the case.... Read More
Microscopic section
microscopic section --> section 1. The act of cutting, or separation by cutting; as, the section of bodies. 2. A part... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Xylem vessel
Definition noun, plural: xylem vessels (botany) One of the tracheary elements of xylem that is characterized by being made... Read More