Search Results for: oxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
How High Sugar Level in Blood Damages the Blood Vessels
By Vicki Mozo Damage in the vasculature is common in individuals who have high sugar level in blood. It seems that an... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Magnetosome
Definition noun, plural: magnetosomes A membranous cytoplasmic structure containing mineral crystals that enable certain... Read More
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin adenine dinucleotides fla·vin ad·e·nine di·nu·cle·o·tide, ad·e·nine... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Human Reproduction
Terminology and Concepts Primary reproductive organs are called gonads - testes in the male and ovaries in the female.... Read More
Inorganic catalyst
Definition noun, plural: organocatalysts An inorganic compound used as a catalyst. Supplement Inorganic catalysts speed up a... Read More
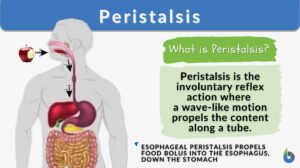
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
Anaesthetic
Definition noun, plural: anesthetics (pharmacology) A drug or an agent that is used to produce temporary and partial loss of... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Microelectrode
Definition noun, plural: microelectrodes An electrode with a tip having dimensions of the order of one micrometer, thereby... Read More
Dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: dinucleotides di·nu·cle·o·tide, daɪ njuːklɪəˌtaɪd An organic compound comprised of two... Read More
Bradykinin
Definition noun A nonapeptide that is vasoactive causing blood vessels to dilate Supplement Bradykinin is a type of kinin.... Read More
Sulfuric ether
sulfuric ether --> diethyl ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3;a flammable, volatile organic solvent used in extraction procedures;... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More