Search Results for: phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Definition noun A type of phosphorylation in which the phosphoryl group is transferred from a donor compound (a... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More
Autophosphorylation
Definition noun (biochemistry) The phosphorylation of the kinase through its own enzymatic... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
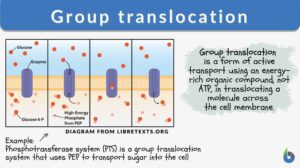
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Adenosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide made up of adenine, ribose, and two phosphate... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
How High Sugar Level in Blood Damages the Blood Vessels
By Vicki Mozo Damage in the vasculature is common in individuals who have high sugar level in blood. It seems that an... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Electron transport chain
Definition noun A group of compounds that pass electron from one to another via redox reactions coupled with the transfer... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
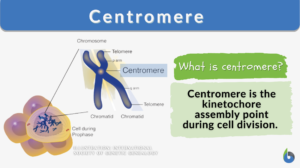
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Adenine nucleotide
Definition noun plural: adenine nucleotides A nucleotide wherein the nucleobase is adenine Details Overview A nucleotide... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More