Search Results for: replication
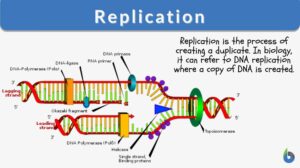
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
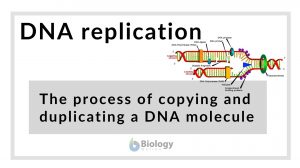
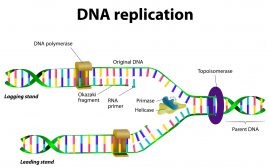
DNA replication
DNA Replication Definition DNA replication is the process of copying and duplicating a DNA molecule. The process is carried... Read More
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is... Read More
Bidirectional replication
Bidirectional replication a type of dna replication where replication is moving along in both directions from the starting... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Single-stranded DNA
What is single-stranded DNA? DNA is the material that living organisms possess that carries their genetic make-up. DNA and... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Okazaki fragment
Definition noun, plural: Okazaki fragments Relatively short fragment of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
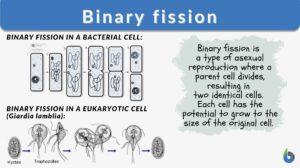
Binary fission
Binary Fission Definition What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a... Read More
DNA polymerase
Definition noun, plural: DNA polymerases (molecular biology) An enzyme assisting in DNA replication Supplement Polymerases... Read More
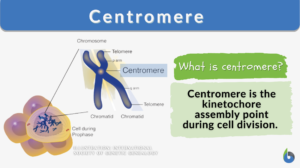
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Synthesis phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase wherein the cell primarily duplicates its DNA via... Read More
Between Necessity and Probability: Searching for the Definition and Origin of Life (Advances in Astrobiology and Biogeophysics)
Between Necessity and Probability: Searching for the Definition and Origin of Life (Advances in Astrobiology and... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
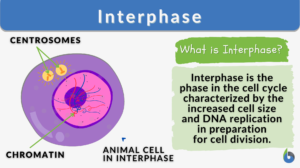
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Rolling circle mechanism
rolling circle mechanism (Science: molecular biology) A mechanism of dNA replication in many viral dNAs, in bacterial f... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
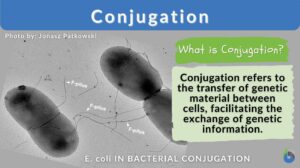
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More