Search Results for: solvent
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Solvent drag
Definition noun, plural: solvent drags The transportation of ultrafiltrate back from the renal tubule through the flow of... Read More
Universal solvent
Definition noun (1) A substance capable of dissolving all or a large variety of substances. (2) An... Read More
Solubility
Definition noun (1) The quantity of a particular substance (solid, liquid, or gas solute) that can dissolve in a particular... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Aqueous solution
Definition noun, plural: aqueous solutions A solution wherein water is the dissolving medium or solvent Supplement Solution,... Read More
Polar solvents
polar solvents Solvent's that exhibit polar forces on solutes, due to high dipole moment, wide separation of charges, or... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Gram-positive bacteria
Definition noun, singular: gram-positive bacterium A group of bacterial cells that retains the violet colour following ... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Volatile oil
Volatile Oil Definition Volatile oils are aromatic compounds that are characterized by their volatility and inability to... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Concentration
Definition noun (1) The measure of the amount of a sub-component (especially solute) in a solution (2) The ratio of the mass... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Sphingolipid
Definition noun plural: sphingolipids sphin·go·lip·id A type of lipid with a sphingoid base (e.g. sphingosine and... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Fatty acid
Definition noun plural: fatty acids'' fatty acid, ˈfætɪ ˈæsɪd Any of the group of a long chain of hydrocarbon... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Deactivation
Definition noun The process of making inactive or the state of becoming less or not active anymore Supplement Deactivation... Read More
Passive transport
Passive transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances such as ions and molecules move down their respective... Read More
Ultrafiltration
Definition noun (1) A high pressure filtration through a semipermeable membrane in which colloidal particles are retained... Read More
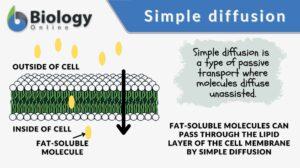
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Stereospecificity
Definition noun Relate to the specific points along the chain of configurations resulting in the spatial arrangement of... Read More





![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)