Search Results for: strands
Complementary strands
Complementary strands (Science: molecular biology) two single strands of dna in which the nucleotide Sequence is such that... Read More
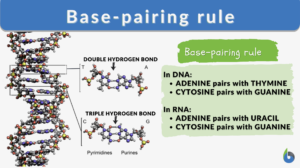
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Single-stranded DNA
What is single-stranded DNA? DNA is the material that living organisms possess that carries their genetic make-up. DNA and... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
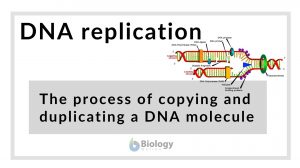
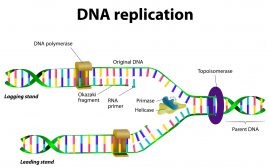
DNA replication
DNA Replication Definition DNA replication is the process of copying and duplicating a DNA molecule. The process is carried... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
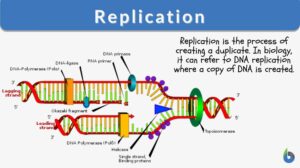
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
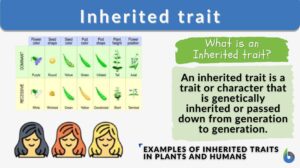
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
DNA polymerase
Definition noun, plural: DNA polymerases (molecular biology) An enzyme assisting in DNA replication Supplement Polymerases... Read More
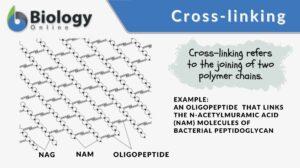
Cross-linking
Cross-linking Definition Cross-linking, in general, means the forming of cross-links between the joining structures. In... Read More
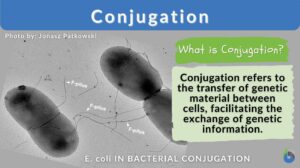
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Renaturation
Definition noun, plural: renaturations (molecular biology) The conversion of denatured protein or nucleic acid to its native... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
Thin filament
Definition noun, plural: thin filaments A type of myofilament that is made up of actin, troponin, and tropomyosin molecules,... Read More
Fibrinogen
Definition noun, plural: fibrinogens A soluble rod-shaped plasma glycoprotein (340 kd, 46 nm long) consisting of six peptide... Read More
Okazaki fragment
Definition noun, plural: Okazaki fragments Relatively short fragment of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA... Read More
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
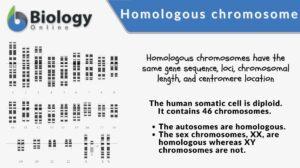
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More