Search Results for: substrate
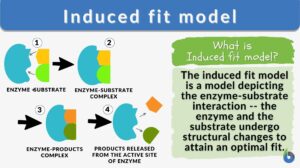
Induced fit model
Induced-Fit Model Definition The induced-fit model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction to depict the dynamic... Read More
Substrate specificity
Definition noun A feature of enzyme activity with regard to the kind of substrate reacting with an enzyme to yield a... Read More
Enzyme-substrate complex
Definition noun A non-covalent complex composed of a substrate bound to the active site of the enzyme. Supplement The... Read More
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Definition noun A type of phosphorylation in which the phosphoryl group is transferred from a donor compound (a... Read More
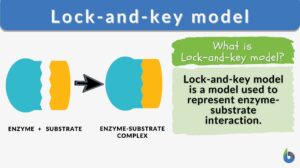
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Respiratory substrate
Definition noun The substance required for cellular respiration to derive energy through... Read More
Active site
Definition noun, plural: active sites The specific region of an enzyme where a substrate binds and catalysis takes place or... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
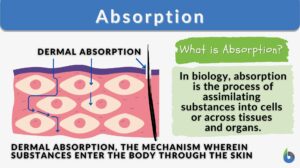
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
Pioneer species
You might have come across news of some barren lands turning into luscious grasslands or forests after decades? Or you might... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
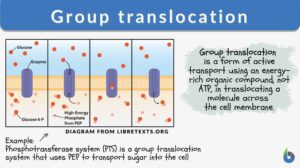
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Michaelis-menten hypothesis
Michaelis-Menten hypothesis (Science: chemistry) That a complex is formed between an enzyme and its substrate (the... Read More
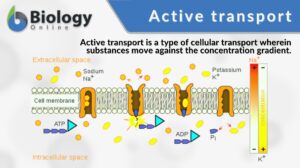
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Elective culture
Elective culture a method of isolating microorganisms capable of utilizing a specific substrate by incubating an inoculum in... Read More
Dehydrogenase
Dehydrogenase (Science: enzyme) enzyme that oxidizes a substrate by transferring hydrogen to an acceptor that is either... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More