Search Results for: activation
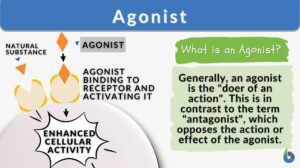
Activation
Definition noun (general) The state or the process of being active and/or effective (biochemistry) The process of making a... Read More
Activation energy
Definition noun The amount of energy (in joules) needed to convert all the molecules in one mole of a reacting substance... Read More
Enzyme activation
Enzyme activation conversion of an inactive form of an enzyme to one possessing metabolic activity. It includes 1)... Read More
Gene activation
Gene activation The process of activation of a gene so that it is expressed at a particular time. This process is crucial in... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
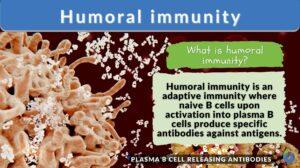
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Deactivation
Definition noun The process of making inactive or the state of becoming less or not active anymore Supplement Deactivation... Read More
Complement
Complement (Science: immunology) a term originally used to refer to the heat labile factor in serum that causes immune... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Antagonistic Muscle
Definition of Antagonistic Muscle What does the term “antagonistic” mean? As the name suggests, the word antagonistic... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
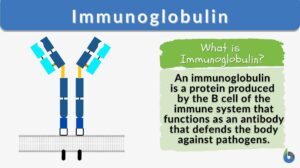
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Kinetic molecular theory
Kinetic molecular theory (Science: chemistry) this theory assumes that molecules must collide in order to react. The more... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
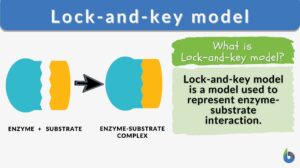
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Coagulation
Definition noun, plural: coagulations (haematology) The process of clot formation (surgery) The disruption of tissue by... Read More
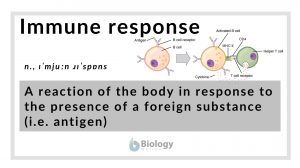
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Fibrinogen
Definition noun, plural: fibrinogens A soluble rod-shaped plasma glycoprotein (340 kd, 46 nm long) consisting of six peptide... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Scratch reflex
Definition noun, plural: scratch reflexes (1) A spinal reflex characterized by a response to the activation of sensory... Read More
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis Definition Spermatogenesis is the biological process of producing sperm cells. It occurs in the male gonad... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More