Search Results for: grain
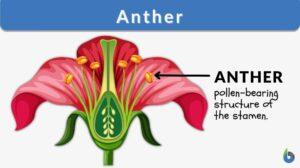
Pollen Grain
What are Pollen Grains? Plants are unique structures and so they carry out mechanisms in special ways. Fertilization in... Read More
Seed Plants
There are two main subdivisions of seed plants—the ones without covered seeds, the gymnosperms, and the ones with covered... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
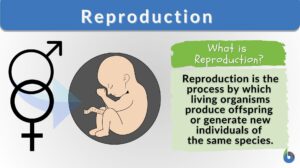
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
Elaioplast
Definition noun, plural: elaioplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores oil Supplement Plastids are organelles involved in... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
saccharomyces cerevisiae (Science: fungus) A species of yeast which is an important model organism for biological study,... Read More
Granulation
Definition noun, plural: granulations (1) The act or process of forming grains or granules, e.g. the granulation of powder... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Alongside the numerous vitamins that are required as part of a healthy diet, we must also eat food containing a variety of... Read More
Collaboration
COLLABORATION A loose asscociation between organisms of the same species such that their activities benefit each other. Eg.... Read More
Chondrichthyes
Definition noun A taxonomic class comprised of cartilaginous fish Supplement Chondrichthyes is taxonomic superclass of... Read More
Crop yield
Definition noun The amount of plant crop (such as cereal, grain or legume) harvested per unit area for a given... Read More
Allopolyploidy
Definition noun (genetics) A type of euploidy wherein the additional set of chromosomes is derived from another species,... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Petrified Wood : The World of Fossilized Wood, Cones, Ferns, and Cycads
Petrified Wood : The World of Fossilized Wood, Cones, Ferns, and Cycads ... Read More
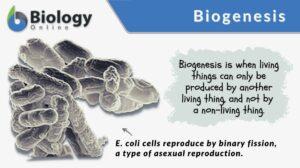
Biogenesis
Biogenesis Definition Biogenesis refers to the idea or the process whereby a living thing comes from another living thing,... Read More
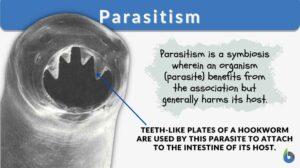
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Udden-wentworth scale
Udden-Wentworth scale (Science: plant biology) A geometric scale of grain sizes which classifies particles of siliciclastic... Read More