Search Results for: inorganic phosphate
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
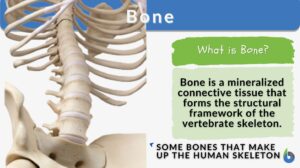
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Glycogenolysis
Definition noun The metabolic process of breaking down stored glycogen in liver into glucose subunits (i.e.... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Inorganic salt
Definition noun, plural: inorganic salts A salt that lacks C-H bonds Supplement A salt is defined as the neutral ionic... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
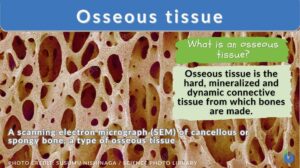
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Bone tissue
Definition noun, plural: bone tissues A mineralized connective tissue from which bones are made. Supplement The bone tissue... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
ATP synthase
Definition noun, plural: ATP synthases An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of ATP from the phosphorylation of ADP with... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Vitreous humor
Definition noun The clear, gel-like body fluid in the vitreous chamber, i.e. the posterior cavity between the lens and the... Read More
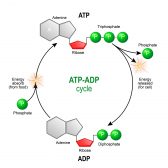
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of an... Read More