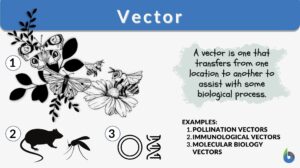
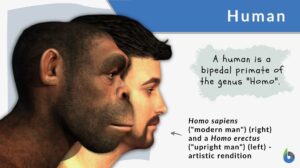
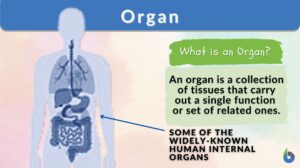
Search Results for: intermediate parts
Intermediate parts
Intermediate part Central portion; the portion located between extreme portions of a structure; an interposed or intervening... Read More
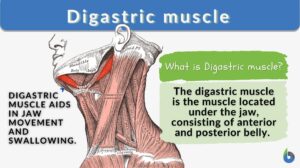
Digastric muscle
Digastric Definition The digastric muscle is a paired muscle located under the jaw, consisting of the anterior and... Read More
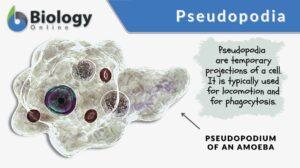
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
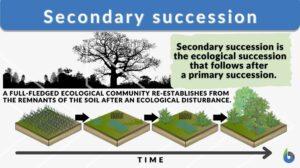
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Skeletal system
What is the Skeletal System? How to define a skeleton? The skeletal system is the main framework that gives your body its... Read More
Skeletal muscle
Definition noun, plural: skeletal muscles A voluntary, striated (vertebrate) muscle that is associated with the skeleton,... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
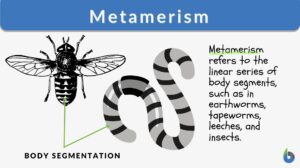
Metamerism
Metamerism Definition Metamerism is the repetition of homologous body segments. This type of development can be seen in the... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Nail matrix
Definition noun The area consisting of mitotically active layer of cells at the base of the fingernail or the toenail and... Read More
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis Definition Spermatogenesis is the biological process of producing sperm cells. It occurs in the male gonad... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Trimorphism
trimorphism 1. (Science: chemistry) The property of crystallizing in three forms fundamentally distinct, as is the case with... Read More
Taenia solium
Definition noun A tapeworm species of class Cestoda, and is commonly known as the pork tapeworm Supplement Taenia solium... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More