Search Results for: metabolite
Metabolite
Definition noun, plural: metabolites A substance that is a product of metabolic action or that is involved in a metabolic... Read More
Androsterone
Definition noun, plural: androsterones A steroid hormone, with a chemical formula of C19H30O2, has masculinizing effects,... Read More
Deoxyadenosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyadenosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Regulatory gene
Definition noun, plural: regulatory genes A gene that is involved in the production of a substance that controls or... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
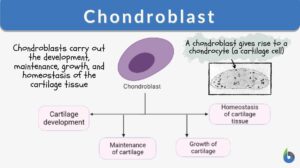
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Hydrogen Acceptor
Any substance that is capable of becoming reduced and accepting hydrogen atoms, which allows the release of energy from such... Read More
Adenine nucleotide
Definition noun plural: adenine nucleotides A nucleotide wherein the nucleobase is adenine Details Overview A nucleotide... Read More
Guanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide made up of guanine, ribose, and two phosphate... Read More
Deoxyguanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Deoxyguanosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Deoxycytidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Activation
Definition noun (general) The state or the process of being active and/or effective (biochemistry) The process of making a... Read More
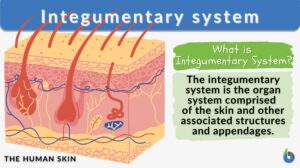
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving the fusion of haploid female gamete (egg cell) and haploid male... Read More
Intracellular fluid
Definition noun The body fluid within the cell composed mainly of water dissolved ions, and other molecules Supplement The... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Progesterone
Definition noun, plural: progesterones A progestogen hormone, with a chemical formula of C21H30O2, naturally produced in... Read More