Search Results for: pancreas
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Islets of Langerhans
Definition Cell clusters in the pancreas that form the endocrine part of that organ; secrete insulin and other hormones.... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
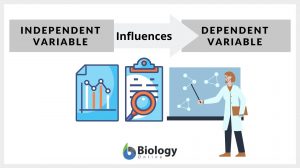
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
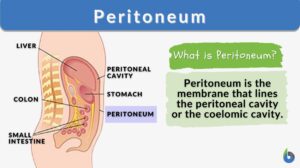
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
Pancreatic lipase
Definition noun, plural: pancreatic lipases A pancreatic enzyme that splits dietary fats by hydrolyzing triacyglycerol... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Pancreatic juice
Definition noun The transparent fluid secreted by the pancreas composed mainly of water, electrolytes, and... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Endocrine gland
Definition noun, plural: endocrine glands Any of the ductless glands secreting hormones that are released directly into... Read More
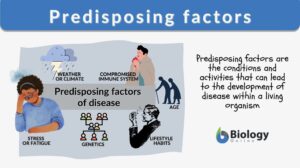
Predisposing factors
All organisms can be born with or develop a disease at any point in their lifetime. When someone is born with a disease, it... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Hormone Production
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system.... Read More
Prolactin-releasing hormone
Definition noun, plural: prolactin-releasing hormones A polypeptide hormone originating in the hypothalamus, and whose... Read More
Cuboidal epithelium
Definition noun, plural: cuboidal epithelia An epithelial tissue comprised of cuboidal epithelial cells, and is involved in... Read More
Digestive Enzymes
Have you ever thought about what happens to the food after you have taken it into your mouth? How those big steak pieces... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Definition noun, plural: simple cuboidal epithelia Simple epithelium composed of cuboidal epithelial cells Supplement A... Read More
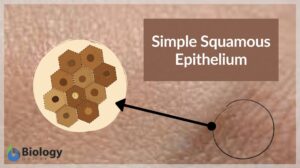
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More