Search Results for: senescence
Senescence
Senescence Definition Senescence is defined as biological aging. In cell biology, it refers to the cell wherein it is no... Read More
Gerontoplast
Definition noun, plural: gerontoplasts A plastid that forms from chloroplast during senescence Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Degenerate
Degenerate means to become worse or less of its kind or former state. In biology, it means an entity performs the same... Read More
Hayflick phenomenon
Definition noun The phenomenon characterized by the limited number of times a normal cell population would divide... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Biological clock
Definition noun, plural: biological clocks Any of the various mechanisms that regulate biological rhythms Supplement A... Read More
Abscission
Definition noun (botany) The normal shedding of a senescent plant part or organ (e.g. old leaf or ripe fruit) (zoology) The... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Reactive oxygen species
Definition noun Chemically reactive molecules and ions of oxygen with an unpaired electron Supplement Reactive oxygen... Read More
Pleiotropy
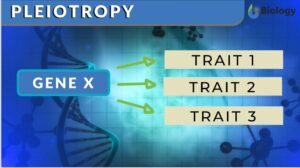
Pleiotropy Definition When one single gene starts affecting multiple traits of living organisms, this phenomenon is known... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More