Search Results for: abundant
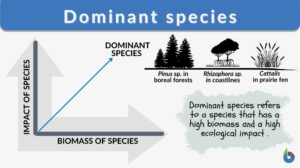
Dominant species
Dominance is the state of being supreme or dominant. Community dominance refers to the form of dominance where certain... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Apparent competition
Competition Definition One of the many branches of biology is ecology. Ecology is the study of the relationships that the... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Biodiversity
The biological world or life on earth is a marvel that has amazed us since time immemorial. The rich natural diversity of... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
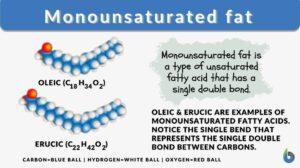
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Charophyta
Charophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live predominantly in freshwater habitats. Members... Read More
Interspecific competition
Interspecific Competition Definition In Biology, competition is defined as the process that occurs among species that have... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Arthropods
There are over two million species of arthropods, who initially arrived on Earth in the middle of the Cambrian period.... Read More
Limiting factor
Limiting Factor Definition A limiting factor refers to any of the factors (variables) in an environment capable of limiting... Read More
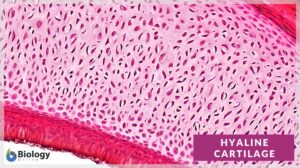
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Phenylalanine
phenylalanine (Science: amino acid) One of the amino acids which the body cannot manufacture itself, but must acquire from... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Loose connective tissue
Definition noun A type of connective tissue proper that holds and binds organs together, and is characterized by its loose,... Read More
Dense connective tissue
Definition noun A type of connective tissue that contains chiefly of collagen fibers (type I collagen) relative to the... Read More