Search Results for: derivative
Derivative chromosome
Derivative chromosome An anomalous chromosome generated by translocation. Synonym: translocation... Read More
Derivative
Derivative a chemical substance derived from another substance either directly or by modification or partial... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Galactosamine
Definition noun, plural: galactosamines A hexosamine, where galactose contains an amine (-NH2) instead of a hydroxyl (–OH)... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Hormone Production
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system.... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
N-acetylglucosamine
Definition noun An amino sugar derivative of glucose, with a chemical formula of C8H15NO6, and serves as a major component... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Diethylaminoethyl-cellulose
Definition noun (1) A positively charged resin used in ion-exchange chromatography for protein purification and... Read More
Amino sugar
Definition noun, plural: amino sugars A sugar molecule the nonglycosidic hydroxyl (–OH) group is replaced by an amine... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Dansyl chloride
Definition noun (chemistry) A strongly fluorescent compound that will react with the terminal amino group of a protein;... Read More
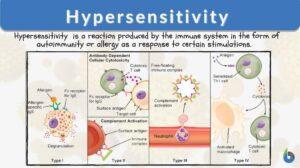
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity Definition Hypersensitivity is the exaggerated immune response to protect the human from foreign bodies... Read More
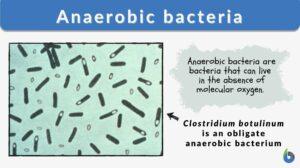
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Diels hydrocarbon
Diels hydrocarbon (Science: biochemistry) a phenanthrene derivative obtained by the dehydrogenation of various... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Biotic potential
When we look at the different forms of life, we often wonder how they have continued to exist one generation after another.... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More