Search Results for: exit
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Nuclear pore
Definition noun plural: nuclear pores ˈnu kli ər, pɔː Any of the many perforations on the nucleus as a result of the... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Nucleoporin
Definition noun plural: nucleoporins Any of the family of porins that make up the nuclear pore complex Details Overview... Read More
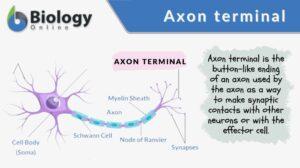
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
External urethral sphincter
Definition noun The urethral sphincter associated with the discharge of urine in both males and females, and where semen is... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
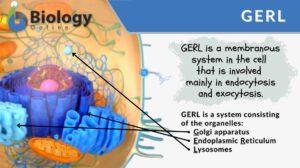
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Selective permeability
Definition noun A feature and a function of the plasma membrane that is essential to maintain homeostasis by regulating the... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
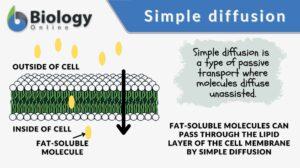
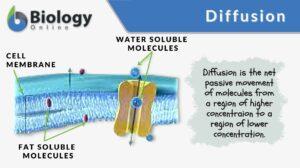
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Cerebrospinal fluid
Definition noun, plural: cerebrospinal fluids A clear, colorless body fluid that fills the ventricles of the brain and the... Read More
Internal urethral sphincter
Definition noun The urethral sphincter made up of smooth muscle cells found at the inferior end of the urinary bladder and... Read More
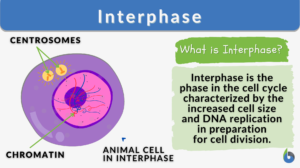
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Anterolateral
Anterolateral Definition Anterolateral is a term used in anatomy to describe the position of a structure as being away from... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Back aperture
Back aperture (Science: microscopy) The exit pupil of a microscope objective lens. The objective lens back aperture, which... Read More
Perinuclear space
Definition noun plural: perinuclear spaces per·i·nu·cle·ar space The space or gap between the inner and outer... Read More
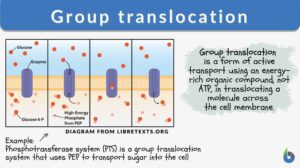
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
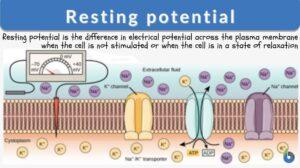
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
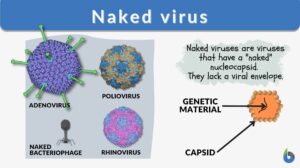
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More