Search Results for: glutamate
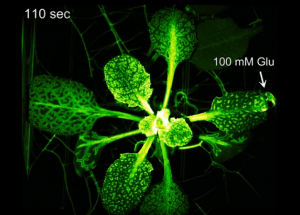
Plant sets off “SOS” for plant defense when it gets hurt
When herbivore, such as an insect, nibbles a plant leaf, the plant sets off an "SOS" or distress signal as one of the... Read More
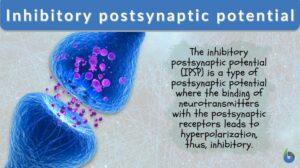
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Components
Component s, glutamate mutase (Science: chemical) component s of the coenzyme b12-dependent glutamate mutase from... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
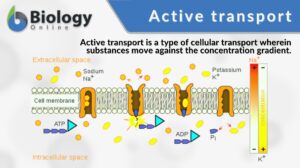
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Isopeptide bond
Definition noun, plural: isopeptide bonds A peptide bond formed between a carboxyl group of one amino acid and an amino... Read More
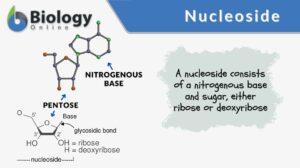
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More