Search Results for: membranous
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Magnetosome
Definition noun, plural: magnetosomes A membranous cytoplasmic structure containing mineral crystals that enable certain... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Chromoplast
Definition noun, plural: chromoplasts Any of the coloured plastids associated with pigment synthesis and... Read More
Endomembrane
Definition noun, plural: endomembranes The membraneous components in a cell, i.e. nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum,... Read More
Visceral cranium
Definition noun The portion of the vertebrate skull derived from the embryonic pharyngeal arches that give rise to mandible,... Read More
Viscerocranium
Definition noun The portion of the vertebrate skull derived from the embryonic pharyngeal arches that give rise to mandible,... Read More
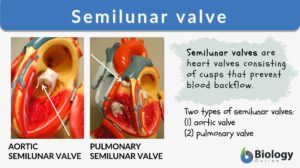
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Lycinibacillus fusiformis
Definition noun A long rod-shaped obligate aerobe organism that is able to utilize oxygen to metabolize numerous sugars... Read More
Magnetotaxis
Definition noun A form of taxis characterized by a directional movement of an organism in response to a magnetic... Read More
Pseudostratified epithelium
Definition noun, plural: pseudostratified epithelia An epithelial tissue comprised of a single layer of epithelial cells... Read More
Stratified columnar epithelium
A stratified columnar epithelium (plural: stratified columnar epithelia) is a type of stratified epithelium in which the... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Seed Plants
There are two main subdivisions of seed plants—the ones without covered seeds, the gymnosperms, and the ones with covered... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Roof of mouth
roof of mouth --> palate 1. (Science: anatomy) The roof of the mouth. The fixed portion, or palate proper, supported by... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Epithelium
An epithelium is a type of animal tissue made up of densely packed cells (called epithelial cells) that rest on a basement... Read More
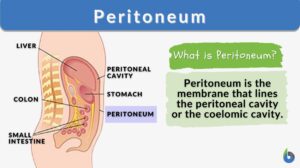
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
Paramural body
Paramural body (Science: plant biology) membranous structure located between the plasma membrane and cell wall of plant... Read More
Pericardium
pericardium (Science: anatomy) A double membranous sac which envelops and protects the heart. The layer in contact with the... Read More
Asteraceae
'Asteraceae'', composite family. A single family enclosed in order Asterales in subclass Asteridae. The other name -... Read More