Search Results for: moves
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
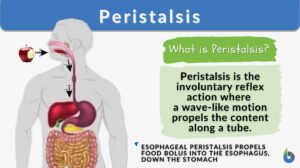
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
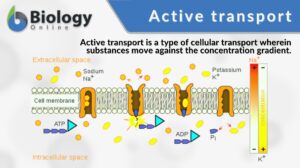
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
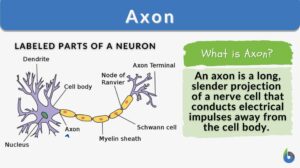
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
Passive transport
Passive transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances such as ions and molecules move down their respective... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Phototaxis
Definition noun A form of taxis characterized by the directional movement of an organism in response to... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Gravitaxis
Definition noun A form of taxis characterized by the directional movement of an organism in response to... Read More
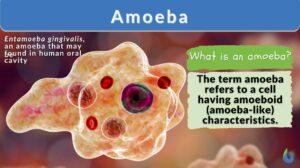
Entamoeba coli
Definition noun A non-pathogenic species of the genus Entamoeba that reside in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and... Read More
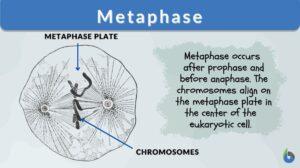
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Thermotaxis
Definition noun A form of taxis characterized by the directional movement of an organism in response to... Read More
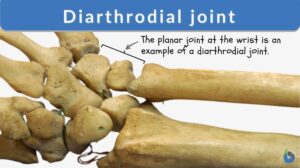
Diarthrodial joint
What is a diarthrodial joint? A diarthrosis joint is a freely moving joint characterized by its mobility and joint cavity... Read More
Magnetotaxis
Definition noun A form of taxis characterized by a directional movement of an organism in response to a magnetic... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
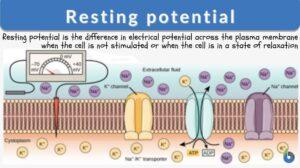
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase
Definition noun A membrane enzyme that allows the diffusion of protons (hydrogen ions) through its proton channel component... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
ATP synthase
Definition noun, plural: ATP synthases An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of ATP from the phosphorylation of ADP with... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Protein Synthesis
If you have jumped straight to this page, you may wish to look at the previous tutorial about DNA, which gives background... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More