Search Results for: protons
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Brown adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: brown adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals that is brownish as opposed to... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
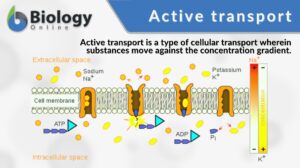
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Dehydrogenation
Pertaining to an oxidised molecule which has had hydrogen removed from it.dehydrogenation The removal of one or more... Read More
Proton gradient
Proton gradient in biology, the proton gradient may be used as an intermediate energy source for heat and flagellar... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
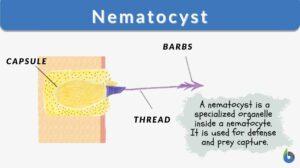
Nematocyst
All organisms are composed of millions of cells. Many cells serve specific purposes and are specialized to do distinct... Read More
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin adenine dinucleotides fla·vin ad·e·nine di·nu·cle·o·tide, ad·e·nine... Read More
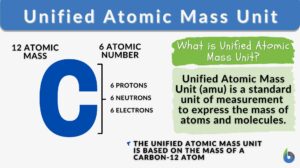
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
Proton-motive force
proton-motive force energy that is generated by the transfer of protons or electrons across an energy-transducing membrane... Read More
Acidophile
Definition noun, plural: acidophiles An organism that can or must live in an acidic environment Supplement An acidophile is... Read More
Flavoprotein
Definition noun, plural: flavoproteins A protein containing a flavin moiety, e.g. flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and... Read More
Atomic mass
Atomic mass (Science: chemistry, physics) The mass of an atom relative to other atoms. The present-day basis of the scale of... Read More
Dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: dinucleotides di·nu·cle·o·tide, daɪ njuːklɪəˌtaɪd An organic compound comprised of two... Read More
Proton donor
proton donor (Science: chemistry) An acid, a susbstance that donates protons in an acid-base reduction... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
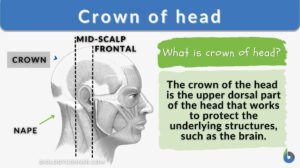
Crown of head
Crown of Head Definition The crown of the head is the upper dorsal part (or area) of the head. Several creatures have... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More