Search Results for: acidic
Acidophile
Definition noun, plural: acidophiles An organism that can or must live in an acidic environment Supplement An acidophile is... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
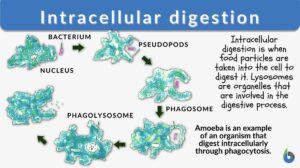
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Digestive Enzymes
Have you ever thought about what happens to the food after you have taken it into your mouth? How those big steak pieces... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
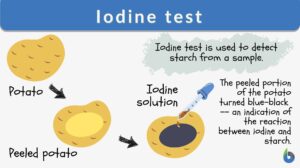
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Ecosystem Succession
Just one of the amazing aspects of life on Earth is that it spreads to all areas where the habitat will allow it to survive.... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Neutrophile
Definition noun, plural: neutrophiles (1) A neutrophilic organism that lives and thrives in an environment with a... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Phagolysosome
Definition noun plural: phagolysosomes (cell biology) A cytoplasmic body that forms from the fusion of phagosome and... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūl A cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
Thermoacidophile
Thermoacidophiles (thermoacidophile, singular) are archaebacteria that can usually be found in very acidic environments that... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Gamma-amylase
'Definition noun, plural: gamma-amylases A form of amylase that cleaves the last alpha-1,4-glycosidic linkages at the... Read More