Search Results for: ammonium
Nitrifying bacterium
Definition noun, plural: nitrifying bacteria A bacterium that is capable of converting ammonium into... Read More
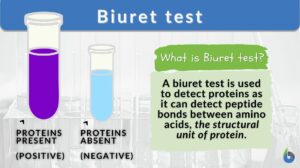
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Nitrification
Definition noun A process wherein a nitro group is added to an organic compound Supplement Nitrification is a process where... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Abiotic Fixation
Definition noun It is part in nitrogen cycle wherein atmospheric nitrogen fixation carries out non-living components to... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Zwitterion
Definition noun, plural: zwitterions A molecule carrying both a positive and a negative charge Supplement A zwitterion is a... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Ammonification
Ammonification the conversion of organic nitrogen to ammonium (NH4+) by the action of decomposers... Read More
Chemoheterotroph
Definition noun, plural: chemoheterotrophs An organism deriving energy by ingesting intermediates or building blocks that it... Read More
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
Chemoautotroph
Definition noun, plural: chemoautotrophs An organism (typically a bacterium or a protozoan) that obtains energy through... Read More
Primary producers
'Primary producers (also called simply as producers) are the autotrophs capable of producing organic compounds from light... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Heterotroph
Heterotroph Definition What is a heterotroph? Does a heterotroph make its own food? In biology and ecology, a heterotroph... Read More
Ammonotelism
Ammonotelism The excretion of ammonia and ammonium ions is calles ammonotelism. The organisms which excrete by ammonotelism... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Nitrogen fixation
Definition noun The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a more usable form by natural means, such as by the... Read More
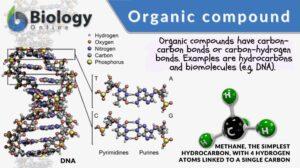
Organic compound
Organic Compound Definition An organic compound is a compound that, in general, contains carbon covalently bound to other... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More