Search Results for: bloodstream
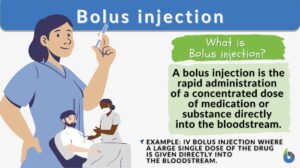
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Glycosuria
Definition noun, plural: glycosuria The presence of atypically high sugar level in urine Supplement Glycosuria is a... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes definition Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs located in different parts of the body and act as... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More
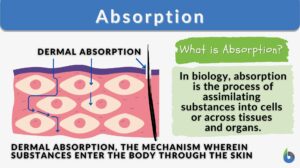
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
White adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: white adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals used to store energy and acts as... Read More
Angiotensinogen
Definition noun An alpha-2 globulin protein that is found in the bloodstream and release into circulation mainly by the... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the... Read More
Pathobiology of allergy and its most severe form, anaphylaxis
When allergy season looms, some people with serious hypersensitivity to allergens tend to be apprehensive of what may come.... Read More
Bloodstream
Definition noun The blood flowing through a circulatory system of an animal, carrying substances from one tissue to... Read More
Dead Man Walking
Dead Man Walking: Wade Davis and the Secret of the Zombie Poison By Patrick D. Hahn Accepted on September 4, 2007 Twenty... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
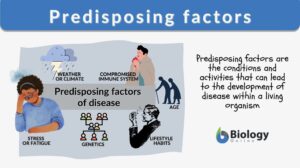
Predisposing factors
All organisms can be born with or develop a disease at any point in their lifetime. When someone is born with a disease, it... Read More
Lymphatic vessel
Definition noun, plural: lymphatic vessels (anatomy) A vessel that carries lymph and is responsible for the removal of... Read More