Search Results for: escherichia coli
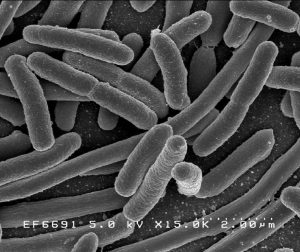
Escherichia coli
Definition A Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped species belonging to the family... Read More
Entamoeba coli
Definition noun A non-pathogenic species of the genus Entamoeba that reside in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
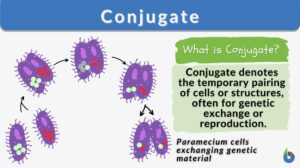
Asexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction Definition What is asexual reproduction? Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not... Read More
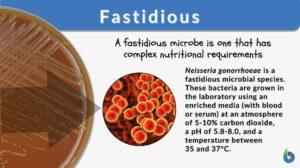
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
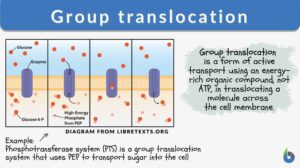
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
DNA polymerase I
Definition noun The first known DNA polymerase, encoded by polA gene, and is involved in DNA replication in... Read More
“Mutualism factor” could explain why body does not attack normal flora
When sadness reeks in and you feel as if you are all by yourself, think again. That is because you are never alone. As a... Read More
Heat-labile
Definition adjective Likely to be altered or degradation when subjected to heat Supplement In chemistry, the lability of a... Read More
Enterobacteriaceae
Definition noun: (taxonomy) A family of gram-negative bacilli that inhabit the large intestine of humans and other... Read More
Specific epithet
Definition noun, plural: specific epithets The second part of the binomial name of a particular species Supplement In... Read More
Okazaki fragment
Definition noun, plural: Okazaki fragments Relatively short fragment of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA... Read More
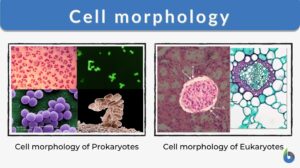
Cell morphology
The basic essence for any living organism is its structural framework which includes appearance, form, and the... Read More
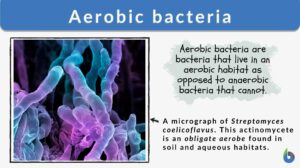
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
DNA polymerase II
Definition noun A DNA polymerase involved in DNA replication in prokaryotes, is encoded by polB gene, and composed of 783... Read More
Heterotroph
Heterotroph Definition What is a heterotroph? Does a heterotroph make its own food? In biology and ecology, a heterotroph... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Bacteriophage
Definition noun, plural: bacteriophages A virus capable of infecting a bacterial cell, and may cause lysis to its host... Read More
Gammaproteobacteria
Definition noun (taxonomy) A class within Phylum Proteobacteria that includes unicellular bacteria that are mostly... Read More
Recombinant DNA
Definition noun Genetically-engineered DNA molecule formed by splicing fragments of DNA from a different source or from... Read More
Binary vector
Definition noun Cloning vector that can propagate in both Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens for use in... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
Induced enzyme
Induced enzyme Inducible enzyme, an enzyme that can be detected in a growing culture of a microorganism, after the addition... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Dna gyrase
Dna gyrase (Science: enzyme molecular biology) a type II topoisomerase of escherichia coli, that is essential for dna... Read More
Gastroenteritis
Definition noun An inflammation of the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, particularly of the stomach and the... Read More