Search Results for: gene regulation
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Some genes are switched on or off depending on environmental conditions. The... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Regulatory gene
Definition noun, plural: regulatory genes A gene that is involved in the production of a substance that controls or... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
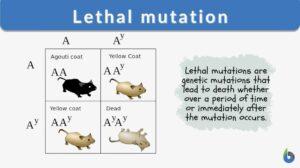
Lethal mutation
Lethal Mutation Definition Genetic mutations come from changes in the DNA structure or sequencing in an organism. Often... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Characteristic
Characteristics Definition We can define characteristics as qualities or features that describe the distinctive nature or... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More