Search Results for: projections
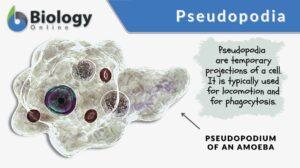
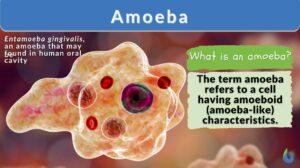
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
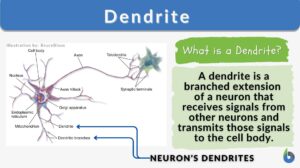
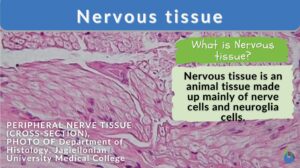
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
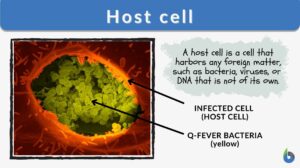
Projections
projection system The system of axons carrying stimuli from one portion of the nervous system to other... Read More
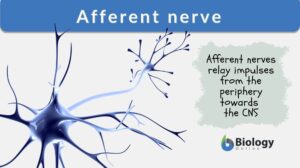
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
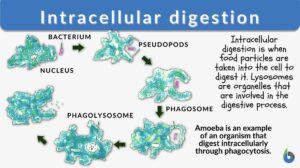
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
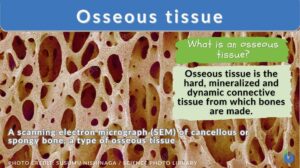
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Microvillus
Definition noun, plural: microvilli Any of the minute hairlike structures projecting from the exposed surface of the cell in... Read More
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
Hirsuties coronae glandis
Definition noun The small bumps on the ridge on certain human glans penis Supplement Hirsuties coronae glandis are small... Read More
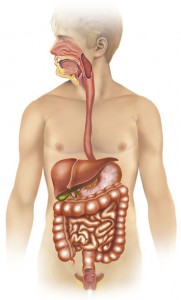
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Areolar gland
Definition noun, plural: areolar glands Any of the sebaceous glands in the areola surrounding the nipple Supplement Areolar... Read More
Digestive Enzymes
Have you ever thought about what happens to the food after you have taken it into your mouth? How those big steak pieces... Read More
Global Carbon Cycling on a Heterogeneous Seafloor
Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are the fundamental elements of life on Earth. Global carbon varies in amount and its... Read More
Greater cornu
Definition noun, plural: greater cornua (anatomy) Any of the pair of larger horns attached to the lateral borders of the... Read More
How Celiac Disease Affects The Digestive System
Celiac disease is a condition that affects the digestive systems of many individuals all over the world, and in this... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
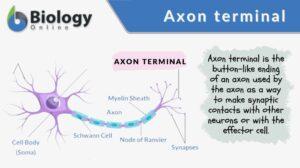
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Blood-brain barrier
Definition noun A semipermeable membrane that serves as a selective barrier separating the circulating blood and the... Read More
External urethral orifice
Definition noun The meatus of the urethra where urine is excreted in both males and females, and where semen is ejected in... Read More
Penile spine
Definition noun, plural: penile spines Any of the spiny projections along the glans or the shaft of the penis Supplement The... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
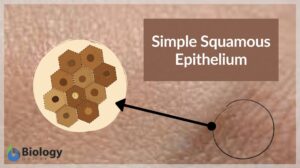
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Hallucination – Are we the only ones “seeing” things or animals hallucinate, too?
Hallucination is defined as perceiving something that seems real but in fact, it is not. Some references take it as a... Read More
Simple columnar epithelium
Definition noun, plural: simple columnar epithelia Simple epithelium composed of columnar epithelial cells Supplement A... Read More












![Hallucinations – a brain glitch – apparently could occur in animals, too. At least, according to a recent experiment on lab mice using optogenetics technique. [Img credit: Rick Harris (Flickr), by CC BY-SA 2.0]](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/hallucination-300x168.jpg)