Search Results for: sweet
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Seed Plants
There are two main subdivisions of seed plants—the ones without covered seeds, the gymnosperms, and the ones with covered... Read More
New Zealand’s Biodiversity
Written by: Maria Victoria Gonzaga Peer-reviewed by: Cathy Buntting, Ph.D. and Andrea Soanes Why is New... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Fauna
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga In the previous lesson, we learned about the high biodiversity of New Zealand and how... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
Beta-amylase
'Definition noun, plural: beta-amylases A form of amylase found in bacteria, molds, yeasts, and the seeds of plants that... Read More
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. The inheritance patterns seen in Mendel's monohybrid and dihybrid crosses... Read More
Why Non-Human Primates Don’t Speak Like Humans
Summary: Why are non-human primates unable to speak like humans? A widely-accepted theory associated it with their lack of... Read More
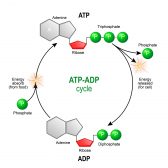
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of an... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Carbohydrates and Fat
Alongside the numerous vitamins that are required as part of a healthy diet, we must also eat food containing a variety of... Read More
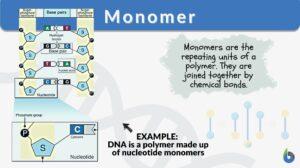
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Glycosphingolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycosphingolipids A type of glycolipid made up of a glycan (or a carbohydrate) linked to the... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More