Search Results for: zero
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Terminal nerve
Definition noun, plural: vagus nerves A small cranial nerve that courses anteriorly along the olfactory... Read More
Mechanical equilibrium
Definition noun A state of a physical system at rest or in unaccelerated motion, and where the sum of all forces and torque... Read More
Carrying capacity
Carrying Capacity Definition What is carrying capacity? In biology and environmental science, the carrying capacity of a... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Zwitterion
Definition noun, plural: zwitterions A molecule carrying both a positive and a negative charge Supplement A zwitterion is a... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
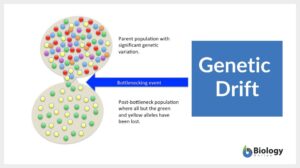
Genetic drift
Genetic Drift Definition What is genetic drift in simple terms? The simple definition of genetic drift ( also referred to... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Wilcoxon rank-sum test
Definition noun A non-parametric test of two samples which support exclusively on the order of observations in which the two... Read More
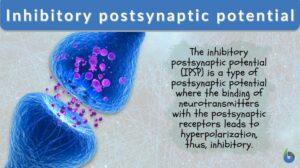
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Realized niche
What is a niche? A niche can be defined as the means by which a species or an individual interacts with its environment. In... Read More
Osmotic Potential
Definition noun (1) The potential of water molecules to move from a hypotonic solution (more water, less solutes) to a... Read More
Discrete random variable
Discrete random variable a random variable that may assume a countable number of values, each with a probability strictly... Read More
Secular equilibrium
secular equilibrium A type of radioactive equilibrium in which the half-life of the precursor (parent) radioisotope is so... Read More
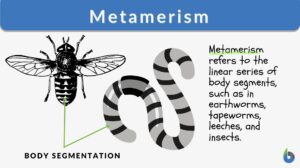
Metamerism
Metamerism Definition Metamerism is the repetition of homologous body segments. This type of development can be seen in the... Read More
Overshoots
overshoot 1. Generally, any initial change, in response to a sudden step change in some factor, that is greater than the... Read More
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
Definition noun A type of postsynaptic potential where the binding of neurotransmitters with the postsynaptic receptors... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
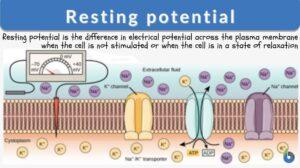
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Boundary layer
Boundary layer (Science: radiobiology) in fluid flow, a narrow region next to a fixed boundary or surface where the fluid... Read More
Moisture content
Definition noun The weight of the water contained in an object or material, usually expressed as a percentage of... Read More
Population Growth and Survivorship
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga Previously, we learned about biodiversity and endemism. Now, let's look at the... Read More