Search Results for: biomolecule
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Flavin mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin mononucleotides fla·vin mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A... Read More
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin adenine dinucleotides fla·vin ad·e·nine di·nu·cle·o·tide, ad·e·nine... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A single nucleotide (as... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Nucleoporin
Definition noun plural: nucleoporins Any of the family of porins that make up the nuclear pore complex Details Overview... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
De novo pathway
Definition noun, plural: de novo pathways (biochemistry) A biochemical pathway where a complex biomolecule is synthesized... Read More
Hemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: hemoglobins A biomolecule made up of haeme (i.e. oxygen-carrying, nonprotein, ferrous component)... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
Organic catalyst
Definition noun, plural: organic catalysts Any organic compound that functions as a catalyst. Supplement Examples of these... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Hemoglobinopathy
Definition noun, plural: hemoglobinopathies A genetic disorder resulting in an abnormal globin structure in the hemoglobin... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Pancreatic juice
Definition noun The transparent fluid secreted by the pancreas composed mainly of water, electrolytes, and... Read More
Spheroprotein
Definition noun, plural: spheroproteins A type of protein characterized by being globular or spherical in shape, and... Read More
Scleroprotein
Definition noun, plural: scleroproteins A type of protein characterized by being fibrous and its function which is to... Read More
Pentapeptide
Definition noun, plural: pentapeptides A peptide containing five amino acids Supplement Peptides are biomolecules that are... Read More
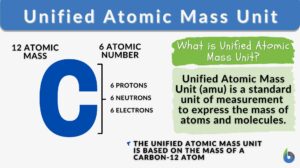
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
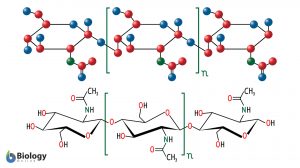
Cellobiose
Definition noun plural: cellobioses cel·lo·bi·ose, ˌsɛləʊˈbaɪəʊz A disaccharide made up of two glucose... Read More
Maltotriose
Definition noun A trisaccharide that has a chemical formula of C18H32O16 and formed from the combination of three monomers... Read More
Glycoconjugate
Definition noun, plural: glycoconjugates A carbohydrate chemically linked to another compound, e.g. lipid or... Read More
Glycolipid
Definition noun, plural: glycolipids A carbohydrate, usually an oligosaccharide, that is covalently linked to a lipid... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More