Search Results for: by-product
By-product
By-product (Science: chemistry) a product of a chemical reaction or industrial process which is different from the desired... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Biorefineries – Industrial Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions
Biorefineries - Industrial Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions ... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
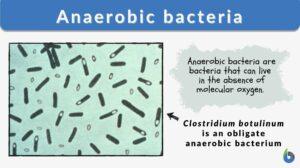
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Metabolite
Definition noun, plural: metabolites A substance that is a product of metabolic action or that is involved in a metabolic... Read More
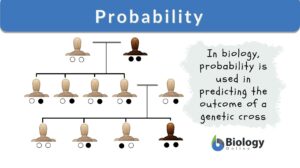
Probability
Probability Definition How do you define probability? In science, probability is a measurement tool that calculates the... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Cell Respiration
As mentioned in the previous tutorial on ATP, the process of respiration is split into 3 distinct areas that occur at... Read More
Photosynthesis – Photolysis and Carbon Fixation
Photosynthesis is the means that primary producers (mostly plants) can obtain energy via light energy. The energy gained... Read More
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology ... Read More
Multiplication
multiplication 1. The act or process of multiplying, or of increasing in number; the state of being multiplied; as, the... Read More
Mass-action ratio
Mass-action ratio The ratio of the product of all of the product concentrations divided by the product of all of the... Read More
End product
End product (Science: biochemistry) The final product of after a series of reactions with enzymes in a biochemical metabolic... Read More
End product repression
End product repression catabolite repression in which the catabolite is an end product of a particular... Read More
Equilibrium constant
Definition noun The ratio in which the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More