Search Results for: c-reactive protein
Reactive oxygen species
Definition noun Chemically reactive molecules and ions of oxygen with an unpaired electron Supplement Reactive oxygen... Read More
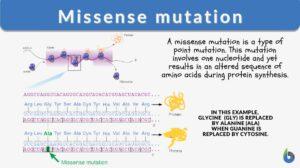
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Phagolysosome
Definition noun plural: phagolysosomes (cell biology) A cytoplasmic body that forms from the fusion of phagosome and... Read More
C polysaccharide
C polysaccharide (Science: microbiology) polysaccharide released by pneumococci which contains galactosamine 6 phosphate and... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Activation
Definition noun (general) The state or the process of being active and/or effective (biochemistry) The process of making a... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More