Search Results for: consumption
Consumption
Consumption 1. The using up of something, especially the rate at which it is used. 2. Obsolete term for a wasting of the... Read More
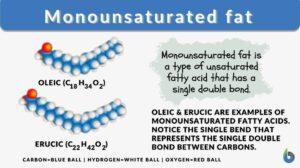
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
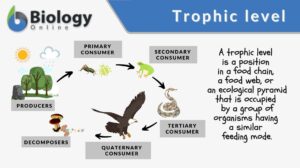
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
Non-sustainability
Non-Sustainability Definition Non-sustainability is the state in which human consumption or activities exceed the ability... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Saturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: saturated fatty acids A form of fatty acid with only single bonds between carbon atoms Supplement A... Read More
Renewable resource
Definition noun A type of natural resource that can be replenished or takes a rather short period of time for nature to... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Teratogenesis
Definition noun The development of structural or functional malformations in an embryo or a fetus Supplement Abnormalities... Read More
Great Oxygenation Event
Great Oxygenation Event Definition The Great Oxygenation Event is defined as the surge of dioxygen (O2) levels in the... Read More
Metabolic rate
Definition noun (1) The rate of metabolism, i.e. the amount of energy used in a certain period. (2) closely approximated* by... Read More
Unsustainability
Definition noun (1) The incapacity of keeping (something) sustainable; the capability of getting depleted (2) The state in... Read More
Unsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: unsaturated fatty acids The unsaturated fatty acid is a form of fatty acid containing one or more... Read More
Homo sapiens sapiens
Homo sapiens What are homo sapiens? Homo sapiens is the species of all the highly developed primates on earth, a category... Read More
Trophic dynamics
Definition noun The system of trophic levels describing the position that an organism occupies, as well as the sequence of... Read More
Sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia
Definition noun The medical or scientific term for brain freeze Supplement The sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia is a type of... Read More
Ecosystem diversity
Ecosystem Diversity Definition What is ecosystem diversity? Ecosystem diversity deals with the study of different... Read More
Carrying capacity
Carrying Capacity Definition What is carrying capacity? In biology and environmental science, the carrying capacity of a... Read More
Tobacco mosaic virus
Definition noun, plural: tobacco mosaic viruses A mosaic virus belonging to genus Tobamovirus that causes mottling and... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Global Carbon Cycling on a Heterogeneous Seafloor
Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are the fundamental elements of life on Earth. Global carbon varies in amount and its... Read More
Biological Viruses
The prime directive of all organisms is to reproduce and survive and this also applies to viruses. Apparently, viruses are... Read More
Freshwater Communities & Lentic Waters
Lentic (still water) communities can vary greatly in appearance, anything from a small temporary puddle to a large lake is... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Arthropods
There are over two million species of arthropods, who initially arrived on Earth in the middle of the Cambrian period.... Read More
The Water Cycle
The water cycle (sometimes referred to as the hydrological cycle) is the continuous transfer of water from air, sea land and... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More