Search Results for: gtp
Guanosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is composed of guanosine (a... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Deoxyguanosine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
Guanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide made up of guanine, ribose, and two phosphate... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Termination
Definition noun (general) The process, act, or state of terminating (biochemistry) A process in which the mRNA synthesis... Read More
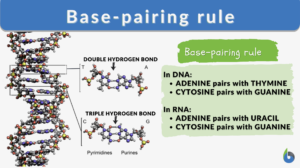
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Nucleoporin
Definition noun plural: nucleoporins Any of the family of porins that make up the nuclear pore complex Details Overview... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxyguanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Cytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis Definition Biosynthesis refers to the production (synthesis) of a complex chemical compound from simpler... Read More
Nuclear pore
Definition noun plural: nuclear pores ˈnu kli ər, pɔː Any of the many perforations on the nucleus as a result of the... Read More
Termination codon
termination codon (Science: molecular biology) The three codons, UAA known as ochre, UAG as amber and UGA as opal, that do... Read More
Elongation
Definition noun (general) The state, act, or process of lengthening Supplement In general, the term elongation refers to the... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
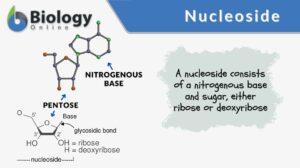
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Initiation
Definition noun (general) The beginning of a state or of a process; the act of initiating Supplement In general sense, the... Read More
Citric Acid Cycle
Definition noun (1) A cycle of reactions catalyzed by enzymes in which pyruvate derived from nutrients and converted to... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More