Search Results for: ingestion
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
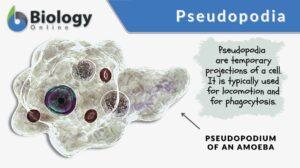
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis Definition What is pinocytosis? Pinocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluids, i.e. the fluid... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
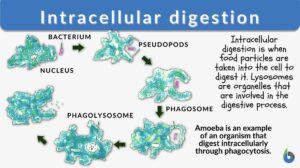
Intracellular digestion
Intracellular Digestion Definition What is intracellular digestion? ‘Intra’ means "inside" and ‘cellular’ pertains... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Nasogastric aspiration
Definition noun An aspiration technique in which the gastric contents are removed or drained using a nasogastric tube that... Read More
Brevibacillus brevis
Definition noun A motile aerobic ellipsoidal spore forming rod organisms involved in gramicidin production an antimicrobial... Read More
Entamoebidae
Definition noun (taxonomy) A family of Archamoebae which includes species such as Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba coli,... Read More
Exogenous antigen
Definition noun Antigen that enters the body of the organism from the outside, e.g. through inhalation, ingestion, or... Read More
Taenia saginata
Definition noun A tapeworm species of class Cestoda, and is commonly known as the beef tapeworm that parasitizes humans and... Read More
Microfilaria
Definition noun, plural: microfilariae The embryonic or early larval stage in the life cycle of certain parasitic nematodes... Read More
Infective stage
Definition noun (parasitology) The stage in the life cycle of an endoparasite wherein it can initiate infection to its... Read More
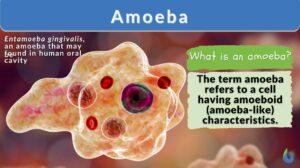
Entamoeba histolytica
Definition noun A disease-causing anaerobic protozoan species capable of causing entamoebiasis and amebic dysentery to its... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Phagolysosome
Definition noun plural: phagolysosomes (cell biology) A cytoplasmic body that forms from the fusion of phagosome and... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
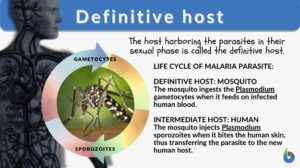
Definitive host
Different Biological Relationships The biological world is interconnected whether we notice it or not. All the life forms... Read More
Incubation period
Incubation Period Definition The incubation period is the time duration between exposure to the pathogen and the appearance... Read More