Search Results for: proton
Proton-motive force
proton-motive force energy that is generated by the transfer of protons or electrons across an energy-transducing membrane... Read More
Protonophore
Definition noun, plural: protonophores The ionophore carrying protons to facilitate crossing the lipid... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Proton gradient
Proton gradient in biology, the proton gradient may be used as an intermediate energy source for heat and flagellar... Read More
Proton donor
proton donor (Science: chemistry) An acid, a susbstance that donates protons in an acid-base reduction... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase
Definition noun A membrane enzyme that allows the diffusion of protons (hydrogen ions) through its proton channel component... Read More
ATP synthase
Definition noun, plural: ATP synthases An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of ATP from the phosphorylation of ADP with... Read More
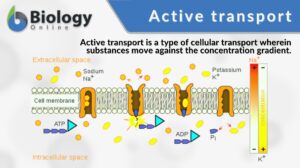
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Chemiosmotic theory
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Electron transport chain
Definition noun A group of compounds that pass electron from one to another via redox reactions coupled with the transfer... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling
Definition noun The process that couples or links the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis. Supplement Chemiosmosis is... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More
Phagolysosome
Definition noun plural: phagolysosomes (cell biology) A cytoplasmic body that forms from the fusion of phagosome and... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More