Search Results for: pump
Sodium-potassium pump
Definition noun A transmembrane ATPase enzyme located in the plasma membrane of animal cells, and functions by pumping... Read More
Protein pump
Protein pump - a kind of protein that is capable of pumping out compounds that could pose a threat to the cell. An example... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
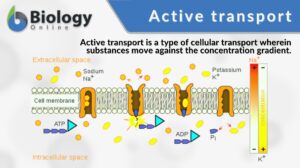
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
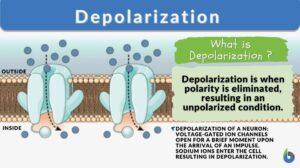
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Definition noun plural: sarcoplasmic reticula (cell biology) The special type of smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
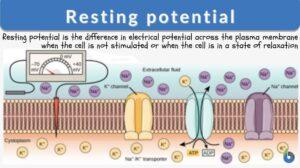
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
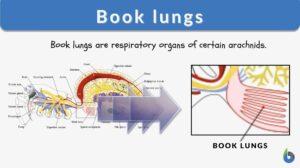
Book lungs
Book Lungs Definition Lungs are known as the organs that help organisms breathe. When we think of lungs, we think of the... Read More
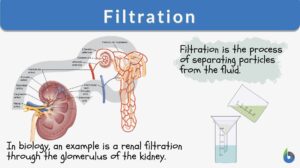
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
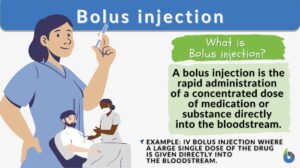
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
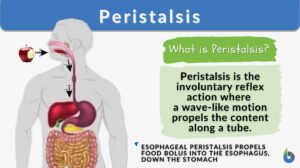
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Single cycle circulation
Definition noun A type of blood circulation in which the system has only one circuit, with the blood being pumped through... Read More
Trabeculae carneae
Definition noun Muscular ridges that crisscross and project from the inner walls of the heart ventricles. Supplement Their... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Global Carbon Cycling on a Heterogeneous Seafloor
Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are the fundamental elements of life on Earth. Global carbon varies in amount and its... Read More
ATP synthase
Definition noun, plural: ATP synthases An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of ATP from the phosphorylation of ADP with... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More