Search Results for: arteries
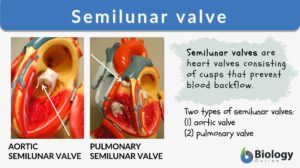
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Blood vessel
Definition noun, plural: blood vessels Any of the vessels in cardiovascular system and functions by carrying blood... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
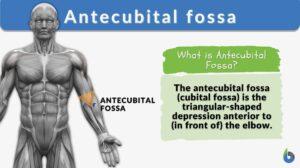
Antecubital fossa
Antecubital Fossa Definition The antecubital fossa or the cubital fossa is the triangular-shaped hollow depression between... Read More
Anterolateral
Anterolateral Definition Anterolateral is a term used in anatomy to describe the position of a structure as being away from... Read More
Spongy bone
Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is a type of bone tissue found at the ends of long bones and... Read More
Human Reproduction
Terminology and Concepts Primary reproductive organs are called gonads - testes in the male and ovaries in the female.... Read More
Elastic fiber
Definition noun, plural: elastic fibers A type of connective tissue fiber that is made up, primarily, of elastin, and found... Read More
Foramen magnum
Definition noun A large opening in the anterior inferior portion of occipital bone in the cranium that serves an outlet of... Read More
Cardiovascular system
Definition noun The organ system in which the blood is pumped through the heart and circulates throughout the body through... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More
Chromaffin cell
Definition noun, plural: chromaffin cells Any of the cells (mostly found) in adrenal medulla and in other ganglia of the... Read More
Heart valve
Definition noun, plural: heart valves (anatomy) Any of the valves of the heart that prevents the back flow of blood through... Read More
Blood pressure
Blood pressure (Science: cardiology, physiology) The force that the circulating blood exerts on the walls of the... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Hemorrhagic exudate
Definition noun A type of exudate that is bloody because of the large component of red blood cells released from ruptured... Read More
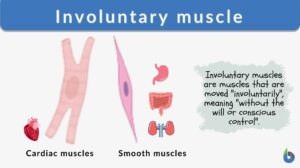
Involuntary muscle
A muscle act typically either under the control of the will or without conscious control. Muscles that can be controlled at... Read More
Penis erection of the
penis, erection of the When the penis fills with blood and is rigid. The penis contains two chambers, called the corpora... Read More
Glycosaminoglycan
Definition noun (biochemistry) The polysaccharide unit of proteoglycan Supplement Glycosaminoglycans are the polysaccharide... Read More
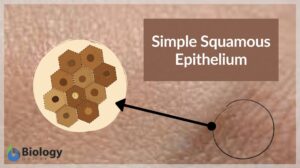
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Greater circulation
Greater circulation --> systemic circulation The circulation of blood through the arteries, capillaries, and veins of the... Read More
Arteriolar sclerosis
Arteriolar sclerosis --> arteriolosclerosis (Science: cardiology, disease) sclerosis and thickening of the walls of the... Read More
Elastic tissue
Definition noun, plural: elastic tissues A connective tissue composed of elastic fibers produced by fibroblasts and can... Read More