Search Results for: hemoglobin
Oxyhemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: oxyhemoglobins A bright red hemoglobin carrying oxygen molecule Supplement One of the main... Read More
Hemoglobinopathy
Definition noun, plural: hemoglobinopathies A genetic disorder resulting in an abnormal globin structure in the hemoglobin... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Hemoglobin
Definition noun, plural: hemoglobins A biomolecule made up of haeme (i.e. oxygen-carrying, nonprotein, ferrous component)... Read More
Red blood cell
Definition noun, plural: red blood cells The blood cell containing hemoglobin and functions primarily to transport... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
A Balanced Diet – Minerals and Proteins
Minerals Various minerals in the Earth's crust are required for a healthy balanced diet. These inorganic compounds have... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More
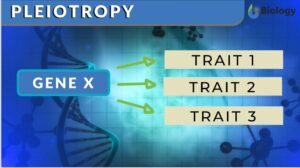
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy Definition When one single gene starts affecting multiple traits of living organisms, this phenomenon is known... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Erythropoiesis
Definition noun, plural: erythropoieses The hematopoiesis of red blood cells Supplement Hematopoiesis is the process of... Read More
Spheroprotein
Definition noun, plural: spheroproteins A type of protein characterized by being globular or spherical in shape, and... Read More
Protein Variety
The sequence of amino acids determines which type of protein it is. It is synthesized from a DNA strand, each DNA strand... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Streptococcus
Definition noun, plural: streptococci (1) A genus of bacteria characterized by being coccus, Gram-positive, and occurring in... Read More
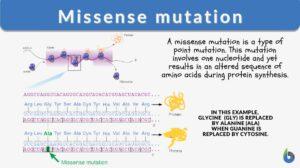
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Monogenic disease
Monogenic Disease Definition A monogenic disease is a diseased condition determined by the interaction of a single gene.... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Macrophage
Definition noun, plural: macrophages A leukocyte whose main function is to eliminate cellular debris and foreign particles... Read More
Mononuclear leukocyte
Definition noun, plural: mononuclear leukocytes A leukocyte characterized by having a nucleus with only one lobe, as opposed... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Granulocyte
Definition noun, plural: granulocytes A leukocyte characterized by the presence of numerous staining granules in the... Read More